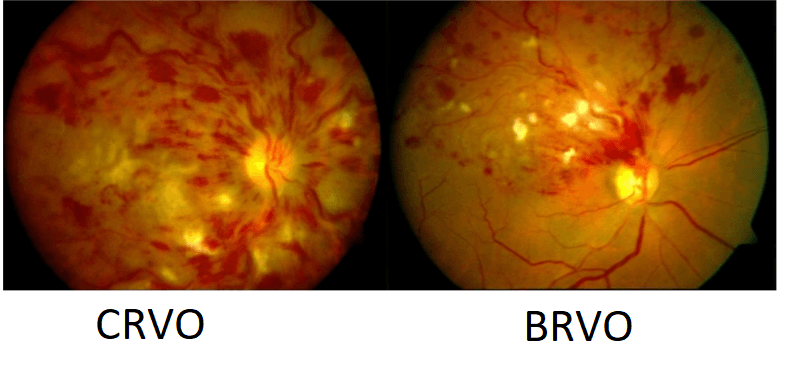
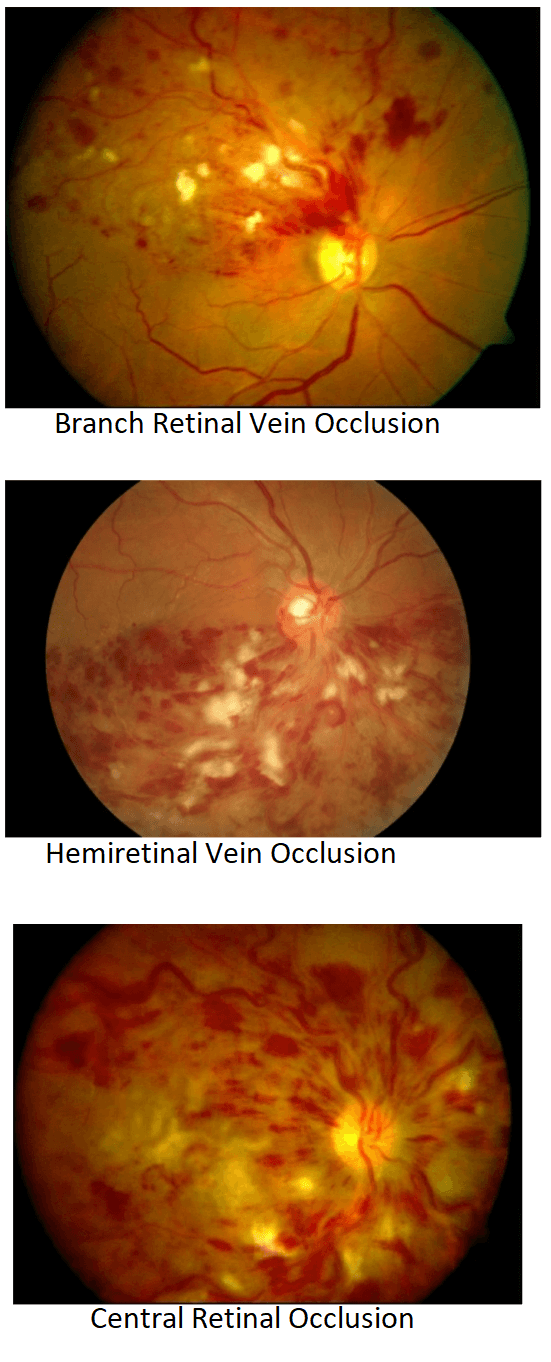
Retinal vein occlusion is a blockage of the small veins that carry blood away from the retina. The retina is the layer of tissue at the back of the inner eye that converts light images to nerve signals and sends them to the brain.
Retinal vein occlusion is most often caused by hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis) and the formation of a blood clot.
Blockage of smaller veins (branch veins or BRVO) in the retina often occurs when retinal arteries that have been thickened or hardened by atherosclerosis cross over and place pressure on a retinal vein.
Because the risk of these disorders increases with age, retinal vein occlusion most often affects older people.
Sudden blurring or vision loss in all or part of one eye
It's important to manage diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol levels. Some patients may receive aspirin or other blood thinners.
The outcome varies. Patients with retinal vein occlusion often regain useful vision.
It is important to properly manage complications, such as macular edema and glaucoma. However, having either of these complications is more likely to lead to a poor outcome.
Call your health care provider if you have sudden blurring or vision loss.
Retinal vein occlusion is a sign of a general blood vessel (vascular) disease. The same measures used to prevent other blood vessel diseases, such as coronary artery disease, may decrease the risk of retinal vein occlusion.
Visit us at Insight Eye Clinic and experience unrivalled professional service from the moment you step in. Our Retinal Vein Occlusion Doctors in Mumbai assure our clients the highest quality retinal treatment.